Article
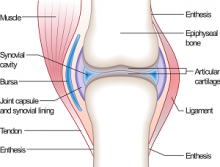
The anatomical place in the body where two bones meet. A joint can either move or be fused. There are three types of joints. A fibrous joint occurs when two bones are connected by fibrous tissue and does not articulate or bend. The skull is an example of bones connected by fibrous joints. Cartilaginous joints occur when bones are connected by cartilage, which allows limited movement between bones. Examples of cartilaginous joints are the connections between the manubrium, the sternum, and the xyphoid process, the are on the chest where the ribs meet at the breast bone. A synovial joint occurs when bones are not directly connected and are therefore able to articulate through a wide range of positions. This movement is facilitated by the lubricating presence of synovial fluid between bones ends. The bones of the fingers, wrists, shoulders, and knees are all examples of synovial joints.
"Synovial Joint Example" by Madhero88 is licensed under CC BY-SA.
Manuscripts
References
Encyclopædia Britannica Online
N.d. Joint. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/305607/joint, accessed June 8,
2016.
Tortora, Gerard J.
1995 Principles of Human Anatomy. New York: HarperCollins College.